1.1 Platforms
This section summarizes the different platforms in which Pyret can run. Most features are available across all platforms, there are some that only work in particular settings.
Elsewhere in the documentation you may see features flagged with
Behavior that is specific to, or works only in, https://code.pyret.org. These typically require using a Google-specific API to access files in Google Drive.
Behavior that is specific to, or works only in, the Visual Studio Code extension.
Behavior that is specific to, or works only in, the command line.
A common combination is:
Behavior that is specific to, or works only in, the Visual Studio Code extension or at the command-line. This typically has to do with accessing the filesystem.
1.1.1 code.pyret.org
The website https://code.pyret.org lets you run Pyret code directly in your browser, and connect to Google Drive to save and share programs you write.
1.1.2 VScode Extension
The Pyret VScode Extension provides a way to run Pyret code within Visual Studio Code in an interface similar to code.pyret.org, with a definitions and interactions area.
1.1.2.1 Installing the VScode Extension
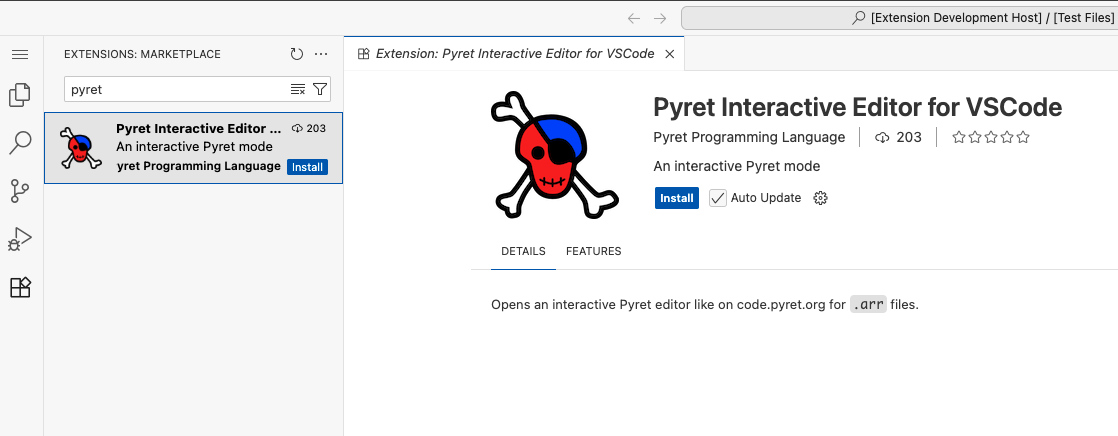
From Visual Studio Code, choose the extensions sidebar options (looks like four squares with the top right square at an angle). Search for “Pyret” and click on the extension called “Pyret Interactive Editor for VScode” by the author “Pyret Programming Language”. You should see a screen like this, with an option to install, which you can click to add the extension:
1.1.2.2 Opening Files in the VScode Extension
The extension can be used from desktop Visual Studio Code, in which case it’s generally expected that students or users are able to open files and folders from their computer in VScode (or get a copy of a folder from version control, etc). Once a folder is opened (for example with File -> Open Folder...), clicking on files with the .arr extension will open them in the editor. Then you can use the Run button and other editor features as usual.
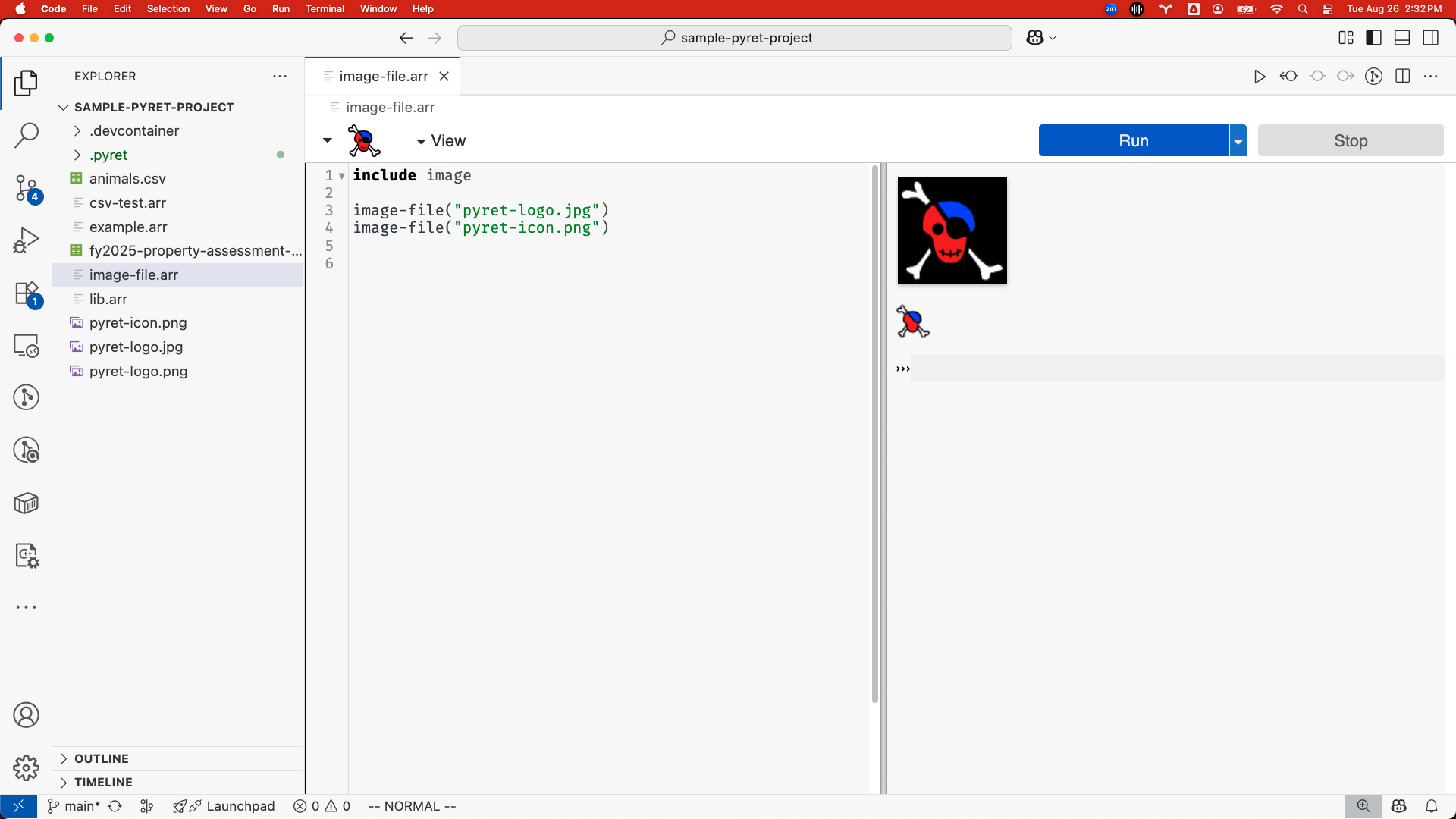
Pyret programs in open editors save and synchronize to the filesystem like other open text files, respecting keyboard shortcuts like Ctrl/Cmd-s or “Save” in the “File” menu. Depending on how VScode is configured autosave may or may not be turned on (it is automatically enabled on github.dev and in Codespaces and not enabled by default in desktop VScode). Look for a dot next to the filename (e.g. my-program.arr •) indicating unsaved changes if you’re not sure.
1.1.2.3 Use with github.dev
The extension can also be used from github.dev. When visiting any Github repository, the keyboard shortcut . (that is, a single period) will open that repository in github.dev, so the repository folder will already be open. (This requires being logged into a Github account.)
In new github.dev workspaces, the extension is not installed automatically. A repository can list recommended extensions: the sample-pyret-project repository gives examples of this, and will make it so users are prompted to install the extension when the workspace opens.
1.1.2.4 Editing Pyret Files with the Default Editor
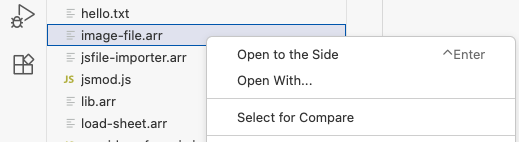
For many reasons we might prefer to edit .arr files without using the visual editor and instead using the Visual Studio Code default text editor. To do this, you can open the context menu on a file and choose “Open With...”, which will allow you select the visual editor or the plain text editor, and optionally set your preferred default:
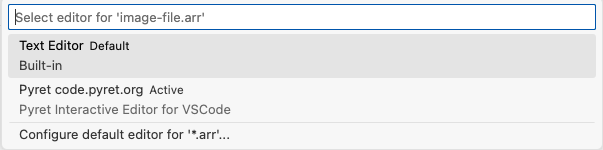
In plain text editors for Pyret files, there is a ▶ icon at the top of the tab. Clicking this button will run the program (like using the run button in the visual editor), and open the interactions area in a new VScode pane to the side.
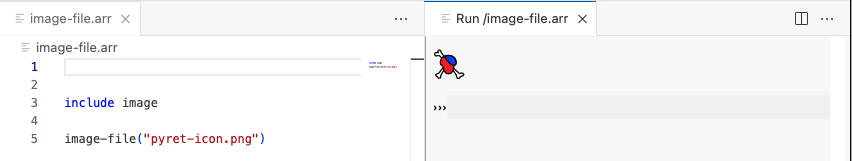
1.1.3 Command Line
Pyret can also be run from the command line. The command-line interface is distributed as a npm package pyret-npm. The options for using the command line are described in the tool itself. The --help option lists the available options.